Cybersecurity Tips for Ethernet Networks
Maintaining a secure Ethernet network is a constant struggle, with new vulnerabilities and exploits being discovered all the time. Steps to prevent unauthorized network access should be based on an IT Security Policy, backed by a proactive approach by network administrators.
The goal of an IT security policy should be twofold: compliance with government regulations, and protection of personal and business data that is stored on the company’s or institutions network. SP 800-171 Rev. 2 “Protecting Controlled Unclassified Information in Nonfederal Systems and Organizations” is a set of U.S. standards for protecting controlled unclassified information in nonfederal systems and organizations.
A Network Security Policy includes a wide array of security types:
- Rules for all users of the network.
- What devices are allowed
- What must be done to secure devices
- How to secure network paths
- How to monitor the network
- How to back up network data
- A Disaster Recovery Plan for in case the network is compromised
Things to Remember for your Ethernet Network
Use Strong Passwords
According to NIST SP 800-171 Rev. 2 Section 3.5.7, a strong password consists of a minimum of 8 characters, with at least one of each: upper case letter, lower case letter, number, and symbol. The password should not include common words (i.e. “potato”), and should not be a commonly used password such as “Pa$5word.”
Physically secure switches and routers
Physical security mean preventing attackers from gaining physical access to the switch or other network devices. Keep network equipment in restricted-access rooms, or in lockable cabinets.
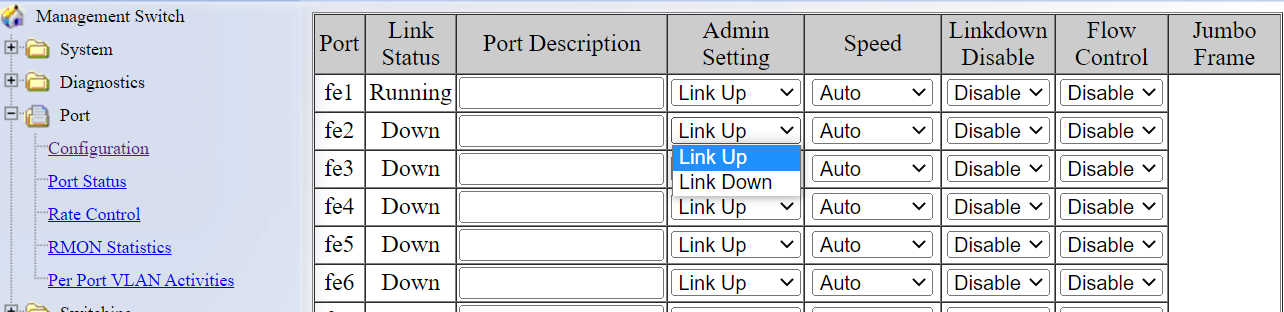
Disable unconnected ports
Disabling unused ports can stop an attacker from connecting to an unused port and gaining unauthorized access to the network. On EtherWAN switches, log into the GUI and navigate to the Port → Configuration screen. Select the unused port and under the field Admin Setting, use the dropdown menu to set the port to “Link Down”. Then save the configuration.
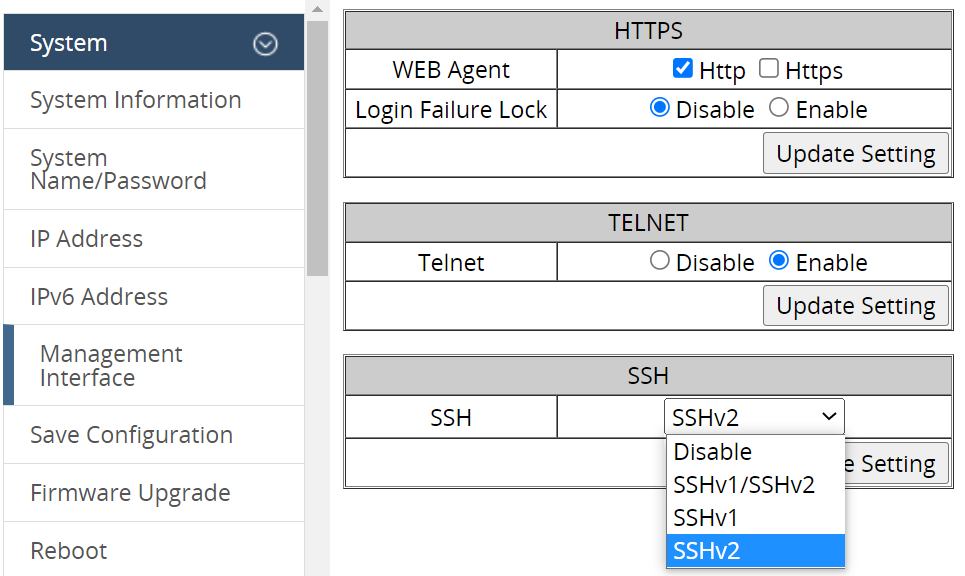
Disable unused management services
HTTP is enabled by default on EtherWAN switches in order to perform configuration via the web GUI. However, HTTP does not encrypt data transmission. Secure connections that require passwords, such as HTTPS and SSH, are more secure means to access and configure a switch. To disable a management interface on an EtherWAN switch, navigate to System → Management Interface, and click the corresponding check box or radio button. Then click Update Setting.
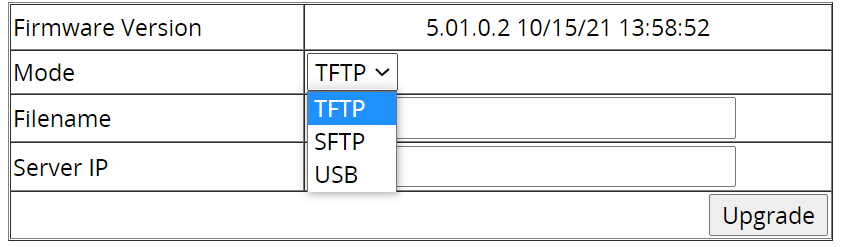
Get the latest firmware for all devices
The process of keeping network devices update never ends. New threats to network security constantly arise, exposing new vulnerabilities. For this reason, it is important to always update networking devices with the latest firmware, in order to protect network devices from the latest attacks.
To upgrade the firmware on an EtherWAN switch, an SFTP or TFTP server is required, or a USB Flash drive with the new firmware file. The firmware file is in a .TGZ or .IMG format. Navigate to System -> Firmware Upgrade, then select the mode and parameters.
Security Requirements for IEC 62443
EtherWAN has addressed cybersecurity for industrial automation and control systems, gained familiarity with IEC 62443, and has gradually become a provider to meet the needs of industrial automation and control systems. These feature requirements can also be found in NIST, ISA, or other leading manufacturers on how to secure user access to the switch and how to secure the switch on the network.
As defined in IEC 62443-1-1, there are a total of seven foundational requirements (FRs), each of which has four security levels (SLs). These SLs are derived from the system security levels defined in IEC 62443-3-3. Here are the details about how EtherWAN security features have achieved and followed certain system security levels based on IEC 62443-4-2.
In order to meet IEC 62443 requirements, especially for IEC 62443-4-2 security certification requirements, EtherWAN has included the switch security features listed in the following table, as well as additional Port Security, SNMPv3, and DoS Protection related security features based on security concerns, to achieve IEC 62443-4-2 different system Security Levels (SLs).
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| MAC Address filtering | Block or allow specific MAC addresses for a port. |
| Enable/Disable Port | Enable or disable network ports of the switch. |
| Storm control (broadcast and multicast) | Monitor traffic levels and drop packets when a specified is exceeded. |
| IEEE 802.1x LAN access control | Set authentication for users and devices. |
| Remote authentication through RADIUS | Allows remote access through a central server. |
| Secure Shell Protocol (SSH) for CLI and Telnet security | Encrypted communications through secure shell. |
| Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) for Web security | Establishes secured links. |
| System log (remote/local) | Logs events and severity. (highest) |
| Access Control Lists (ACL) | Create lists to selectively admit or reject inbound traffic. (highest) |





