What is VLAN and how it works
A LAN is a grouping of two or more devices on a network. A VLAN is a virtual LAN, a subgroup within a local network. VLANs make it easy for network administrators to separate a single switched network into multiple groups to match the functional and security requirements of their systems.

In the above diagram, one switch is supporting two virtual networks–two VLANs. The users on VLAN-10 cannot access the devices on VLAN-20, and vice-versa.
However, VLANs are entirely virtual. They can be implemented without having to run new cables or make major changes in the existing network infrastructure.
VLANs vs. LAN
| Network Parameters | LAN (Local Area Network) | VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | High | Low |
| Devices | Hubs, switches, and routers | Switches and bridges |
| Network Segmentation | Not allowed | Allowed |
| Broadcast Traffic | Prone to broadcast congestion | Reduces broadcast traffic |
| Management | Simple (Single network) | Advanced (Multiple network) |
| Isolation | Lacks inherent isolation | Provides isolation between multiple VLANs |
| Security Configuration | Basic (Relying on external measures) | Offers granular security control through policies |
| Flexibility | Confined to physical infrastructure | Circumvents the physical limitations |
| Scalability | Requires extensive infrastructure changes | No infrastructure changes needed |
| Resource Allocation | Inefficient | Enhances resource and network efficiency |
| Failure Domain | Single | Multiple |
Read More
* Difference between Layer 2 managed switches and Layer 3 managed switches?
* Managed vs. unmanaged switches: How to Choose?
Types of VLANs: Port-Based VLAN and Tagged VLAN
For multiple VLANs to communicate with each other, a router is required. Routers between VLANs filter broadcast traffic, enhance Network security, perform address summarization, and mitigate network congestion.

The two types of VLANs are port-based (untagged) and tagged. For tagged VLANs, a special “tag” is inserted into packets so that switches and routers will forward those packets correctly. The standard supported by most networking devices for supporting VLANs on Ethernet networks is IEEE 802.1Q. This standard adds a tag of four bytes to an Ethernet frame. This extra information identifies the frame as belonging to a VLAN, and contains the VLAN ID number (up to 4094 VLANs are possible on the same network). Multiple tagged VLANs can use the same port on a switch, called a trunk port.
Untagged VLANs are based on the physical ports on a switch (called access ports). There is no extra information added to the Ethernet frame. Instead, each port on the switch is defined as belonging to a specific VLAN. This approach divides a single physical switch into multiple logical switches. If a device is connected to a port in a single VLAN only, then the port should be untagged.
Port-based VLAN

Tagged VLAN

There is a third type of VLAN port called a hybrid port. This option allows for both devices and trunking to occur. Wireless access points are often configured using hybrid ports.
How does a VLAN work
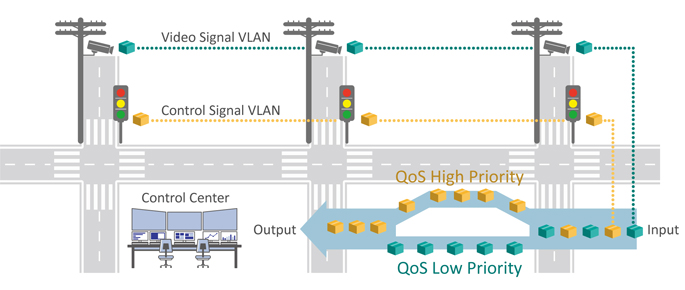
Using VLAN Segmentation and Separation to Improve an ITS Network, one real-world example where VLANs are very useful is in ITS (Intelligent Transportation System) applications. ITS network transmission data includes critical traffic control signals, security surveillance video streams, and digital sign board data. Different data types have different urgencies and data security requirements. When there is a conflict between different types of data, critical traffic control signals must have the highest transmission priority, and this data must not be dropped. For this purpose, it is recommended to use VLANs for data separation and QoS (Quality of Service) classification. The traffic control signal data, on its own VLAN, will be assigned a high priority level so that the transmissions will be given priority when network traffic is heavy.
The Management VLAN
The management VLAN is a single network shared by all switches, no matter how many other VLANs exist on the network. For security, a specific port can be assigned to the management VLAN so that only the administrator is able to log in to that port. Specific MAC addresses (devices) can be listed to have access. This prevents an intruder for gaining access to the network just by connecting a new device. Note that if a management VLAN is misconfigured, the administrator or technician can lose access to that switch and the switch will have to be reset to factory default settings in order to access it again.
Benefits of VLAN segmentation
- Optimizing Network Performance:
VLANs improve network performance by reducing the size of broadcast domains. In a broadcast domain, every device can send packets to every other device, and every packet must be received and processed. This becomes problematic when a broadcast domain becomes very large, leading to degraded switch performance due to the high volumes of broadcast data. With VLANs, these issues are mitigated, as they segment the network into smaller, more manageable units. This optimization leads to a significant boost in overall network efficiency. - Enhancing Security:
VLANs offer an additional layer of security. For instance, a specific VLAN can be created for users with specific security clearances. This means that sensitive data and systems can be isolated from the general network, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. By creating these security-specific VLANs, organizations can better safeguard their critical assets. - Simplified Device Management:
VLANs make device management easier. If a user moves to a new physical location, the physical workstation of that user does not need to be reconfigured. Also, if a user stays in the same location but changes jobs, only the VLAN membership of the workstation needs to be changed.
In summary, VLANs enhance switched network performance by curbing broadcast traffic and bolstering security. They extend beyond a single switch through trunk ports and accommodate various port configurations. For businesses and organizations, VLANs streamline network efficiency, security, and device management, making them essential in modern networking strategies. By segmenting your network into separate VLANs, you can achieve even greater control and optimization. For more in-depth information on using VLAN segmentation and separation to improve your network, visit this resource.
Read More
* How to using VLAN Segmentation and Separation to Improve an ITS Network
* Discover the Benefits of Gigabit Switch: User Experience, Use Cases, and Applications
* Hardened / Industrial Layer 3 Ethernet switches
* How to pick the right Industrial Ethernet Switch for critical networks





